01 Pages : 1-8
Abstract:
This study investigates the impact of Shared Vision (SV) on Responsible Innovation (RI) and Sustainable Competitive Advantage (SCA). Moreover, the level of education is used as a moderator between SV and RI. RI is the process of taking into account the potential ethical, social, and environmental impacts of new technologies and innovations and making sure they are developed and used in a way that is beneficial to society. This can include considering how new products and services will affect different groups of people, and taking steps to mitigate any negative impacts they may have. It also involves engaging with stakeholders and considering their perspectives in the innovation process. SEM technique was used, and data were collected from 1018 respondents from the manufacturing sector. The results explain that SV is significantly related to RI, and RI determines SCA. Furthermore, the level of education moderates the relationship between SV and RI. Moreover, this study provides the general public and various policyholders with an overview of the various levels to which manufacturing SMEs are embracing RI
Key Words:
Responsible Innovation, Level of Education, Manufacturing SMEs, Shared Vision, Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Introduction
Since companies are increasingly expected to create value not just for a small number of shareholders but also for all stakeholders ranging from employees to the whole society, responsible innovation (RI) and sustainable competitive advantage (SCA) have received significant recognition in the literature (Owen et al., 2013). RI is gaining importance in business literature, especially in Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) (Gonzales-Gemio et al., 2020). SCA refers to the capacity to generate value for all stakeholders in a way that is challenging for competitors to replicate, whereas RI refers to the consideration of social, ethical, and environmental impacts of new products, services, and business models (Halme & Korpela, 2014).
A crucial idea that is closely related to RI and SCA is called SV. Aligning organizational goals and values with stakeholder expectations and needs is referred to as SV. A company is more likely to accomplish both RI and SCA when it has a distinct and widely held vision for responsible innovation(Gonzales-Gemio et al., 2020). However, it is unclear how the level of education might moderate this relationship and how SV, RI, and SCA relate to one another. The study examines how SV affects RI and SCA and how education level may moderate this relationship. The idea of RI has gained popularity recently as consumers expect businesses to take into account how their goods and services will affect society and the environment. Companies are seen as using RI as a means of generating value for all parties involved. Companies can create value for all stakeholders and succeed in the long run by taking into account how their goods and services affect people and the environment(Jensen, 2001).
SCA is a crucial idea for businesses because it refers to the capacity to generate value for all stakeholders in a way that is challenging for rivals to match. Companies that achieve SCA are better able to sustainably create value for all stakeholders over time, which increases their chances of long-term success. A crucial idea that is closely related to RI and SCA is SV. A company is more likely to accomplish both RI and SCA when it has a distinct and widely held vision for responsible innovation. SV is crucial because it guarantees that every employee of a company is working toward the same objective and because it gives people a sense of direction and purpose. SV can also aid in bringing stakeholders' needs and expectations into line with the objectives and principles of the organization (Hoe, 2007). However, it is unclear how the level of education might moderate this relationship and how SV, RI, and SCA relate to one another. The study inquires how SV affects RI and SCA and how education level may moderate this relationship. The following are the research questions of the study:
RQ1. Does SV affect RI?
RQ2. Does RI affect SCA?
RQ3. Does the level of education significantly moderates between SV and RI?
Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
The theoretical framework used in this study is dynamic capabilities theory which focuses on how organizations acquire and sustain a competitive advantage over time (Baškarada & Koronios, 2018). It implies that businesses with the capability to change continuously in response to outside factors like market demands or shifts in technology are more probable to gain and keep a competitive advantage (Sirmon et al., 2007). According to the theory, organizations can acquire a set of dynamic capabilities that will allow them to sense, seize, and reorganize both internal and external resources in order to react to environmental changes (Martinelli et al., 2018). These skills include the capacity to recognize and react to changes in the marketplace, establish and manage organizational routines, establish and use networks, and create and manage knowledge (Teece, 2014). The theory of dynamic capabilities also emphasizes how organizational vision, strategy, and culture influence the creation and application of dynamic capabilities (Ambrosini & Bowman, 2009). It implies that organizations are better equipped to develop and use dynamic capabilities to establish and maintain a competitive advantage if they have a clear SV, a well-articulated strategy, and a supportive culture (Salas et al., 2012). The relationship between SV, RI, and SCA in SMEs of a developing Country is being investigated in this study using the dynamic capabilities theory. In particular, SV is a type of dynamic capability that is a crucial accelerator of RI, which then results in SCA.
SV is crucial for SMEs as they have short hierarchies as compared to large companies; therefore, strategies are easy to implement (Aragón-Correa et al., 2008; Khurana et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2022; Strese et al., 2018). Several studies reported that SV is related to social responsibility, which enhances competitive advantage (Torugsa et al., 2012). Furthermore, environmental initiatives, performance, and competitive advantage in SMEs all showed positive correlations with social responsibility and sustainability practices (Burlea-Schiopoiu & Mihai, 2019; Leonidou et al., 2017; Li et al., 2019). Additionally, research on developing nations revealed that innovation in SMEs creates a long-lasting competitive advantage (Arsawan et al., 2020; Quaye & Mensah, 2019). It was further argued that innovation in sustainability contributes to SMEs' ability to gain and maintain a competitive advantage (Burlea-Schiopoiu & Mihai, 2019). Additionally, it was mentioned that ethical innovation could aid SMEs in enhancing their competitiveness (Gonzales-Gemio et al., 2020; Hadj, 2020).
Thus following are the proposed hypotheses:
H1. SV determines RI.
H2. RI determines SCA.
H3. The level of education moderates the relationship between SV and RI.
Methodology
There are three constructs in this study SV, RI, and SCA. SV was gauged through four items (Jehn, 1995; Oswald et al., 1994). RI was examined via five dimensions; anticipation (five items), inclusion (seven items), reflexivity(six items), and responsiveness(nine items) Zhang et al. (2019). At the same time, knowledge management(three items) were from (Lubberink et al., 2017). Similarly, SCA was gauged via five items (Mady et al., 2021). The population of the study is composed of manufacturing SMEs. The information was gathered from the capital cities of Punjab province, as most of the SMEs are in Punjab. A simple random sampling technique was employed, and 1018 responses were used. Fig. 1 demonstrates the research framework.
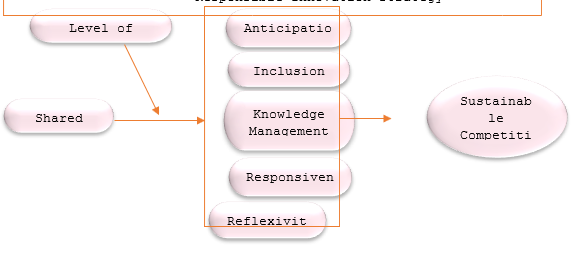
Data Analysis and Results
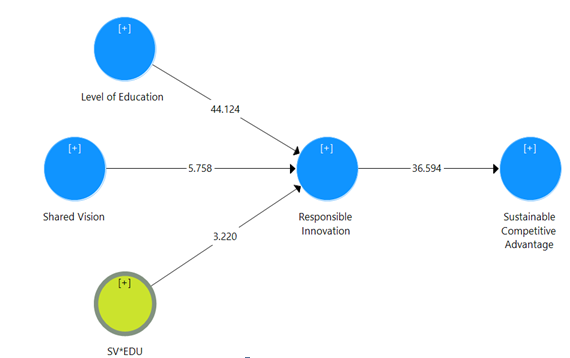
To test the hypotheses, we used SmartPLS 3.3.3 and the SEM methodology. The measurement model is supported by numerous reliability and validity tests (Becker et al., 2022); results reported that all the values of loadings, AVE, CR, alpha, VIF, and R2 are above the required threshold (Hair et al., 2014). Furthermore, HTMT values are in accordance with the required thresholds (Henseler et al., 2015). The structural model results shown in Table 1 depict that SV is significantly related to RI (?-value= 0.112, t-value=5.758). Similarly, RI is significantly related to SCA (?-value= 0.742, t-value=36.594); thus H1 and H2 are braced. Moreover, the level of education significantly moderated the relationship between SV and RI (?-value= 0.047, t-value=3.220); therefore, H3 is supported. Fig. 2 depicts the structural model.
Table 1. Hypotheses Testing
|
Hypotheses |
Relationships |
? -Value |
t-values |
p-values |
Status |
|
H1 |
SV ?
RI |
0.112 |
5.758 |
0.000 |
Yes |
|
H2 |
RI ?
SCA |
0.742 |
36.594 |
0.000 |
Yes |
|
H3 |
SV*EDU ?
RI |
0.047 |
3.220 |
0.002 |
Yes |
Discussions & Conclusion
The findings shed important light on how SMEs in developing nations relate to SV, RI, and SCA. According to the study, RI, SV, and SCA are all significantly correlated. The significance of SV as a catalyst for RI and the function of RI in achieving SCA are highlighted by this. The study also discovered that the relationship between SV and RI is moderated by one's level of education. This implies that companies with higher educational attainment may be better able to create and apply SV to propel RI. This is in line with earlier research, which revealed that education and training are crucial for the growth and application of dynamic capabilities (Eisenhardt & Martin, 2000). Similarly, previous research reported the same results; for instance, it was reported that SV is significantly associated with green innovation (Min & Galle, 2001; Wu & Chen, 2018). Saunders et al. (2014) reported that innovative SMEs are more likely to have SV. Similarly, Suriyankietkaew and Avery (2016) argued that SV is significantly related to organizational performance in the case of Thai SMEs. Hansen et al. (2020) in their study argued that learning orientation, i.e., SV, is significantly related to RI. Furthermore, San Ong et al. (2021) argued that environmental innovation mediates between SV and SCA.

The findings add to the scant literature on RI in the SMEs of developing nations. This study highlights the need for additional research in this area and gives an overview of the various degrees to which manufacturing SMEs are embracing RI. Furthermore, it is crucial to be aware of the study's limitations, which include its small sample size and singular industry sector focus. By gathering data from a larger and more varied sample of organizations and looking at RI in other industry sectors, future research could build on this study. Future studies could also look into the relationships between SV, RI, and SCA, as well as other potential moderating factors. As a result, this study significantly advances our knowledge of how SV, RI, and SCA interact in the context of SMEs in developing nations. It emphasizes the value of RI in achieving SCA as well as the role of SV in advancing RI. Additionally, it implies that organizations with higher education levels may be better able to create and apply SV to promote RI.
This study has a wide range of practical applications. First, the results suggest that for organizations to promote RI and achieve a long-term competitive advantage, they should concentrate on creating SV. This means that businesses should spend time and money developing a common vision that is consistent with their mission, values, and objectives. In order to ensure that their vision is fully understood and embraced, organizations should also make sure that it is effectively communicated to all of their employees, stakeholders, and partners. Second, the results of the study imply that organizations with higher educational levels may be better able to create and apply SV to propel RI. This suggests that businesses should spend money on programs for employee education and training to help them become more dynamic and promote RI. Thirdly, the study sheds light on the extent of RI adoption in SMEs in a developing nation. This information may help organizations and authorities put into action plans to promote RI in this particular setting. Finally, the study's findings are consistent with the notion that RI is a critical component of long-term competitive advantage. As a result, businesses should concentrate on integrating responsible innovation practices into their long-term strategies and daily operations.
In conclusion, this study emphasizes the value of RI, employee education, and SV for achieving SCA. To achieve a long-term competitive advantage, it is also suggested that organizations should concentrate on integrating RI practices into their strategy and operations.
References
- Ambler, T., & Barrow, S. (1996). The employer brand. Journal of Brand Management, 4(3), 185–206
- Arachchige, B. J. H., & Robertson, A. (2013). Employer Attractiveness: Comparative Perceptions of Undergraduate and Postgraduate Students. Sri Lankan Journal of Human Resource Management, 4(1), 33.
- Backhaus, K., & Tikoo, S. (2004). Conceptualizing and researching employer branding. 9(5), 501–517.
- Bakan, İ., Erşahan, B., & İbrahim, K. A. Y. A. (2016). Örgütsel kimliğin ve örgütsel prestijin, örgütsel vatandaşlık üzerindeki etkisi: bir alan araştırması. Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi, 6(1), 69-88.
- Barrow, S., & Mosley, R. (2011). The employer brand: Bringing the best of brand management to people at work. In John Wiley & Sons.
- Behrends, T., Baur, M., & Zierke, L. (2020). Much ado about little: A critical review of the employer branding concept. mrev management revue, 31(1), 1-30.
- Belt, J. A., & Paolillo, J. G. (1982). The influence of corporate image and specificity of candidate qualifications on response to recruitment advertisement. Journal of Management, 8(1), 105-112.
- Berthon, P., Ewing, M., & Hah, L. L. (2005). Captivating Company: dimensions of attractiveness in employer branding. International journal of advertising, 24(2), 151-172.
- Best, John W., Kahn., & James V. (2006). Research in Education. United States of America: Pearson Education Inc.
- Boeije, H. R. (2010). Analysis in Qualitative Research. Sage Publications, London.
- Boyatzis, R. E. (1998). Transforming qualitative information: Thematic analysis and code development. Sage.
- Braun V., & Clarke V. (2016). (Mis) conceptualizing themes, thematic analysis, and other problems with Fugard and Potts' (2015) sample-size tool for thematic analysis. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 19(6), 739–743.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative research in psychology, 3(2), 77-101.
- Bretz Jr, R. D., Ash, R. A., & Dreher, G. F. (1989). Do people make the place? An examination of the attraction-selection- attrition hypothesis. Personnel psychology, 42(3), 561-581.
- Cable, D. M., & Graham, M. E. (2000). The determinants of job seekers' reputation perceptions. Journal of organizational Behavior, 21(8), 929-947.
- Chhabra, N. L., & Sharma, S. (2014). Employer branding: strategy for improving employer attractiveness. International Journal of Organizational Analysis.
- Collins, C. J., & Stevens, C. K. (2002). DigitalCommons ILR the Relationship Between Early Recruitment-Related Activities and the Application Decisions of New Labor-Market Entrants : A Brand Equity Approach to Recruitment The Relationship Between Early Recruitment- Related Activities and the Ap. ILR Collection.
- Colquitt, J. A. (2001). On the dimensionality of organizational justice: a construct validation of a measure. Journal of applied psychology, 86(3), 386.
- Crain, M. G. (2009). Managing Identity: Buying into the Brand at Work Washington.
- Crain, M. G. (2009). Managing Identity: Buying into the Brand at Work Washington.
- Creswell. J. W. (2009). Research Design, Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Method Approaches, 3rd Edition, Sage Publications Inc.
- Dutton, J. E., Dukerich, J. M., & Harquail, C. V. (1994). Organizational images and member identification. Administrative science quarterly, 239-263.
- ElDin Aboul-Ela, G. M. B. (2016). Employer branding: What constitutes "An Employer of choice? Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 11(1), 154–166.
- Fugard A. J., & Potts, H. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: a quantitative tool. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 18(6), 669–684.
- Gilliver, S. (2009). Badenoch & Clark guide. Employer Branding Essentials, 4(3), 35- 50.
- Guest G, Bunce A., & Johnson L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods. 18(1), 59–82.
- Guest, G., MacQueen, K. M., & Namey, E. E. (2012). Validity and reliability (credibility and dependability) in qualitative research and data analysis. Applied thematic analysis. London: Sage Publications, 79-106
- Highhouse, S., Zickar, M. J., Thorsteinson, T. J., Stierwalt, S. L., & Slaughter, J. E. (1999). Assessing company employment image: An example in the fast food industry. Personnel Psychology, 52(1), 151-172.
- Jain, N., & Bhatt, P. (2015). Employment preferences of job applicants: unfolding employer branding determinants. Journal of Management Development, 34(6), 634- 652.
- Judge, L. M., & A., S. T. (2004). Employee attitudes and job satisfaction. 43(4), 395– 407.
- Judge, T. A., Bono, J. E., & Locke, E. A. (2000). Personality and Job Satisfaction : The Mediating Role of Job Characteristics. 85(2), 237–249.
- Katz, D. (1960). The functional approach to the study of attitudes. Public Opinion Quartefi, 24,163-204.
- Kucherov, D., & Zavyalova, E. (2012). HRD practices and talent management in the companies with the employer brand. European Journal of training and Development, 36(1), 86-104.
- Leekha, C. N., & Sharma, S. (2014). Employer branding: strategy for improving employer attractiveness. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 22(1), 48–60.
- Lievens, F., & Scott, H. (2003). Institutional Knowledge at Singapore Management University The relation of instrumental and symbolic attributes to a company's attractiveness as an employer. Research Collection Lee Kong Chian School of Business, 56(1), 75–102.
- Lievens, F., Anseel, F., Lievens, F., Hoye, G. Van, & Anseel, F. (2007). Framework Organizational Identity and Employer Image : Towards a Unifying Framework.
- Love, L. F., & Singh, P. (2016). Workplace Branding : Leveraging Human Resources Management Practices for Competitive Advantage Through "Best Employer" Surveys Workplace Branding : Leveraging Human Resources Management Practices for Competitive Advantage Through '“Best Employer â€â€™ Sur. March.
- Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook. Sage.
- Moroko, L., & Uncles, M. D. (2008). Characteristics of successful branding success as a. 16(3), 160–175.
- Rai, A. (2020), "An application of the instrumental-symbolic framework in Maritime industry: A study on employer branding among seafarers", Management Research Review, Vol. 43 No. 3, pp. 270- 292.
- Roubille, C., Richer, V., Starnino, T., McCourt, C., McFarlane, A., Fleming, P., & Gulliver, W. (2015). Evidence-based recommendations for the management of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis: expert opinion of the Canadian Dermatology- Rheumatology Comorbidity Initiative. The journal of rheumatology, 42(10), 1767-1780.
- Sengupta, A., Bamel, U., & Singh, P. (2015). Value proposition framework: implications for employer branding. Decision, 42(3), 307-323.
- Terjesen, S., Vinnicombe, S., & Freeman, C. (2007), "Attracting Generation Y graduates: Organisational attributes, likelihood to apply and sex differences", Career Development International, 12(6), 504-522.
- Theurer, C. P., Tumasjan, A., Welpe, I. M., & Lievens, F. (2018). Employer Branding: A Brand Equity-based Literature Review and Research Agenda. Internationalournal of Management Reviews, 20(1), 155–179.
- Theurer, C., Welpe, I., & Lievens, F. (2016). Employer Branding : A Brand Equity- based Literature Review and Research Agenda.
- Turban, D. B., & Cable, D. M. (2003). Firm reputation and applicant pool characteristics. Journal of Organizational Behavior: The International Journal of Industrial, Occupational and Organizational Psychology and Behavior, 24(6), 733-751.
- Turban, D. B., & Keon, T. L. (1993). Organizational attractiveness: An interactionist perspective. Journal of applied psychology, 78(2), 184.
- Van Hoye, G., & Saks, A. M. (2011). The instrumental-symbolic framework: Organisational image and attractiveness of potential applicants and their companions at a job fair. Applied Psychology, 60(2), 311-335.
- Van Hoye, G., Bas, T., Cromheecke, S., & Lievens, F. (2013). The instrumental and symbolic dimensions of organisations' image as an employer: A large-scale field study on employer branding in Turkey. Applied Psychology, 62(4), 543-557.
- Woodruffe, C. (2006). "A potent secret for winning a crucial edge over your rivals?", Industrial and Commercial Training, 38 (1), 18-22.
Cite this article
-
APA : Riaz, A., & Ali, F. H. (2022). Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model. Global Economics Review, VII(III), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2022(VII-III).01
-
CHICAGO : Riaz, Adil, and Fouzia Hadi Ali. 2022. "Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model." Global Economics Review, VII (III): 1-8 doi: 10.31703/ger.2022(VII-III).01
-
HARVARD : RIAZ, A. & ALI, F. H. 2022. Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model. Global Economics Review, VII, 1-8.
-
MHRA : Riaz, Adil, and Fouzia Hadi Ali. 2022. "Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model." Global Economics Review, VII: 1-8
-
MLA : Riaz, Adil, and Fouzia Hadi Ali. "Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model." Global Economics Review, VII.III (2022): 1-8 Print.
-
OXFORD : Riaz, Adil and Ali, Fouzia Hadi (2022), "Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model", Global Economics Review, VII (III), 1-8
-
TURABIAN : Riaz, Adil, and Fouzia Hadi Ali. "Responsible Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Moderated Mediation Model." Global Economics Review VII, no. III (2022): 1-8. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2022(VII-III).01
