Abstract:
This study is conducted to assess the impact of heads' leadership and team management competencies on teachers' job satisfaction at the university level. Mixed method research was used to conduct the study. Four universities of Rawalpindi and Islamabad were randomly chosen. Four deans of social sciences, 40 heads of social sciences, and 175 faculty members were chosen as the sample. Deans of social sciences were interviewed for qualitative aspects. Two questionnaires were developed, one for heads and the other for teachers for quantitative analysis. Statistical and descriptive evidence of the study concluded that heads' leadership and team management significantly contribute towards teachers’ job satisfaction level.
Key Words:
Leadership Styles, Team Management Competencies, Job Satisfaction, Motivational Level, Creative Climate, Problem-solving
Introduction
In the process of molding the individual's life, the essential source is the vast vision towards the leadership competency of the teacher in the educational environment. Leadership combined with the team management and their impact on job satisfaction is the new upcoming stream in the area of research. The relevance of leadership, team management, and job satisfaction is essential for a better educational environment (McShane & Glinow, 2004). Educators in any nation have credit to the mental development of individuals. Job satisfaction improves the quality of an educator by means of internal relaxation which improves his or her skills in education specifically in the teaching field. To increase the national developmental benefits of any nation, the teachers' enthusiasm is necessary, which can be developed by the state through providing internal satisfaction and motivation to teachers (Bateman & Snell, 2002).
To understand the effects of leadership and team management, it is essential to understand the indicators of the leadership and team management that are involved in having an impact on faculty members' job satisfaction. Some of the educational leaders working as head of the department suggested that the task-oriented behavior is more reliable leadership of the departmental head this task-oriented behavior is closely related to the autocratic approach of the head, while other educational leaders suggested that the considerate behavior is more reliable leadership of departmental head this considerate approach is closely related to the democratic approach of the head (Bateman & Snell, 2002).
Styles of leadership practices by the departmental heads in an educational environment those been observed over the years are instrumental, expressive, destination-oriented, authoritative, democratic, transactional, transformational as well as autocratic. But the most observed styles are autocratic, democratic and laissez-faire. The prior obligation of the departmental head is to support the decisions of subordinates in a democratic manner and for the progress of the department with the help of team management practices (Lunenburg & Ornstein, 2011). Departmental heads also need them to equip themselves with new emerging ideas of departmental management. In this study, the major concern is on the autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire characteristics of the leader. While the employees in several ordinary organizations are opposed and dissatisfied with the autocratic leadership style. On the other hand, the task assigned by the leader who practices democratic approach is warmly accepted by the subordinates and generates optimistic feelings in employees. The democratic environment generates a sense of responsibility among the group of subordinates in a way that subordinates perform their duties even in the absence of the leader. The democratic approach has the elements of participative method, which enable the employees and subordinates to perform their duties even if the head is not on-site to guide how to perform (Sweeney & McFarlin, 2002).
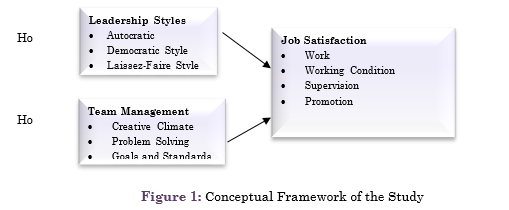
Application of management practices provides proper use of existing resources that is also the optimized use of available resources within the organization. Team management models differ from each other, but there is a very rare possibility of a model that best fits to the organization, but the ideas from different theories can be adopted to achieve new ideas or method that can be followed. The management theory should be employee-centered (Zembylas & Papanastasiou, 2006). Figure 1 presents the conceptual framework of the study.
Objectives of the Study
The following objectives were formulated for investigation.
1. To identify the leadership and team management competencies of university heads.
2. To explore the level of job satisfaction of university teachers.
3. To measure the impact of leadership and team management competencies of university heads on the teachers’ job satisfaction.
Delimitations
Delimitations of this study were as follows:
1. Four Public sector universities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi.
2. Deans of Social Sciences faculties.
3. Heads and Teachers of social sciences faculties.
Review of Literature
Concept of Leadership
Educational researchers and experts provided diversified concepts of leadership. Educational researchers provided several operational definitions regarding how they perceived leadership in an educational context. Leadership is a widespread concept, and it can be viewed differently in different contexts. Different researchers provided varied concepts and definitions of leadership (Lunenburg & Ornstein, 2011). House et al. (2002) provided an acceptable description of leadership which is "the capability to inspire, encourage and assist individuals in collaborating and cooperating to the achievement and efficiency of the organization with which they are associated". The major hazards or intimidations to the leadership practices are the community effects and environmental effects.
Leadership competency is attained by several heads of the organization, but fewer are aware to deploy this competency effectively. Leadership competency can be attained and practiced by any individual working in the organization (Bennis & Nanus, 1985). Casimir (2001) explained the style of leadership as "a design and outline of the influence of the leadership strategies and practices which a leader experienced while performing the leading roles in the organization".
Team Management Concept
Previously, it was specified that in order to accomplish a task when the compulsions for teachers are to interact with another, then that group of teachers forms a "team." As Margerison & McCann (1995) have pointed towards the characterization of a team, they indicated that a team cannot be categorized in the form of experienced guides' groups, mentors, and counselors. According to these investigators, team members greatly interact with one another; they are mindful of their personal strengths and flaws and perform their work in great collaboration. Teamwork can be promoted by raising the cooperativeness between collaborative groups. Basically, team management is an art of assembling and setting together with the resources of all the teachers which are intellectual and are still in service of the institution, it cannot be indicated as uprooting the ideas of the heads of the institutes into the teachers’ minds (Margerison & McCann, 1995). By analyzing the term team management Swift (1972) indicated that it is the sharing of power and duties in an organizational pattern by the managers to their juniors or co-workers. Littlejohn (1982) stated about collaboration and cooperation of organizational individuals, which is the outcome of managing strategies of the team, regardless of the designation of the individual. The management of the teams also helps the members in performing organizational tasks effectively; it assists the leadership strategies of heads as well as resolves the departmental issues by using effective procedures. In the opinion of Owens (1987), creativity and initiative are revealed by the involvement of ego.
The Role of Head in Team Management at Higher Level
Management Functions
Team management is a critical factor in leadership, as it is obligatory for each team leader to have enough skills to perform in the group; he must have the sense of observation power to run a group so that the team may achieve its desired goals. Undoubtedly, it is the role of a team leader who leads a group towards success, as he is the one who creates a good atmosphere in the team or institution. The behavior of team workers and their tasks as well is directly affected by the behavior of the principal. It is the principal who encourages his team members in order to get their high-level performance (Margerison & McCann, 1995). Group management needs enough time of the principal to reach its targeted goals; he must be an expertise and have complete awareness about managing the team members.
Creating Organizational Climate
According to Sergiovanni & Starrat (1979) discussion, there are a lot of administrators, who do not favor the role of leadership as it demands their full attention in an organizational atmosphere, so instead of their selves, they must prefer the tasks related to the institution. This kind of attitude makes the availability of the total number of leadership talent limited in the institution. They were of the opinion that the atmosphere of an organization has significant importance because it permitted the supervisors or principals to directly deal with educational problems when needed and also find out the talent of leadership in others'. There is an incompatibility between team management and a closed climate. To make a successful management team, it is an important element for a principal to be committed to his tasks, such as in the creation of an open climate in the institution.
Problem Solving
To sort out the problems such as differences in opinion, idea sharing, and informing one another normally, a team can only be considered effective if it makes good use of the process of communication. By representing a good dealing of time and energy of the principal, it was observed that these efforts could improve the process of communication. The role of the principal is to facilitate and improve the communication; it is to form the channels which are formal for the communication's upward, downward, horizontal, and diagonal movement and to make it possible by providing related people the accurate information with the required speed and efficiency. To create an open communication climate, a principal must arrange periodic sittings so that the teachers can share their ideas and talk over the problems they are facing with their colleagues and principal also. They further stated that these kinds of consultations are necessary; otherwise, to a common goal, the group tasks get less systematized and less dedicated (Reece & Brandt, 1999).
Goals and Standards
Those decisions and solutions which are made individually have less chance of success if forced by the principals. When a principal takes a decision individually and imposes it to its members, then only he would be considered responsible for that decision, and consequently, for taking the individual decision, he would not be committed to the implementation of the decision. But if he includes all the staff members in the problem-solving method, then all of them will strongly commit to their decision and will check over its effective implementation (Margerison & McCann, 1995). The members of an effective team are only involved in those matters which affect their duties. All the members of the team are referred and participate in problem solving procedure, in setting the policy, and decision-making. By involving in these processes, the team members consider their selves important and improve their potential and encouragement.
Concept of Job Satisfaction
The assessment of workplace practices that lead to an individual's delightful and optimistic mental approach towards the job is categorized as job satisfaction. The mixture and grouping of intellectual and emotional responses regarding the awareness regarding the expected workplace experiences and actual workplace experiences provides the scale and rate of an individual's job satisfaction. While referring to the educational environment, an educator's job satisfaction provides several factors such as teacher's optimistic affection to instructional activities as well as the observed association of expected paybacks of a teaching job and availed paybacks of a teacher (Zembylas & Papanastasiou, 2006).
Conversely, the criteria of satisfying the needs and necessities of an individual could differ from other colleagues. For instance, one individual may feel comfortable with the offered wages and seems uncomfortable regarding the administration standards of the institution or organization. Importance indicators that are generally used by investigators for measuring the satisfaction level of employees are wages, upgradation, nature of work, interpersonal relations with colleagues, working climate, and effectiveness of administrational standards (Lawler, 1973).
Methods
This study was conducted to explore the impact of leadership and team management on the job satisfaction of university teachers. The study was mix method in nature consisting of quantitative and qualitative aspects to explore the effects of leadership and team management. For the quantitative aspect, questionnaires were used. The participants of the questionnaire were university-level heads and teachers working in Rawalpindi and Islamabad cities. The deans of social sciences of the selected universities were interviewed for the qualitative analysis.
Research Design
Sequential explanatory mix method design was used to conduct this particular study; both quantitative and qualitative aspects were considered in the process. The participants for quantitative aspects were heads and teachers, for qualitative analysis, deans of social sciences were selected.
Population
The population contained the heads and teachers of social sciences faculties of selected universities of Rawalpindi and Islamabad and deans of social science faculties. The population of the study were consisted of 42 department heads of social sciences disciplines, 398 teachers, and six social sciences deans. Furthermore, two universities were reserved for pilot testing, which were excluded from the overall population.
Sample and Sampling
In order to get a maximum presentation of the respondents in the study stratified random sampling technique was used. Two strata were made based on heads and teachers of social sciences faculties, respondents were selected through a proportional allocation from respective strata. The selection of participants from four universities is supported by the standards provided by Krejcie & Morgan (1970) and later the standards supported and cited by Gay (2000). Forty heads and 175 faculty members were selected through a proportionate stratified random sampling technique. For interview four social sciences deans from sampled universities were selected. Table 1 shows the sample size of the study:
Table 1. Sample Size from Selected Institutions
|
S. No |
Universities |
Deans |
Heads |
Faculty |
|
1 |
Pir Mehr Ali Shah Arid
Agriculture University Rawalpindi |
1 |
5 |
11 |
|
2 |
International Islamic
University Islamabad |
1 |
15 |
53 |
|
3 |
National University of Modern
Languages, Islamabad (NUML) |
1 |
6 |
30 |
|
4 |
Quaid-i-Azam University,
Islamabad |
1 |
14 |
81 |
|
Total |
4 |
40 |
175 |
|
Instruments
An interview was developed for qualitative aspects, which were deans of social science faculties. On the other hand, two questionnaires were developed. The first questionnaire was administered to the heads to measure the leadership styles and team management competencies. The second questionnaire was administered to the faculty members to measure the job satisfaction level.
Data Collection and Analysis
The researcher personally visited the sampled universities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi for data collection. The interviews of social sciences deans were personally administered by the researcher to collect responses from dean respondents to fulfill the study. Furthermore, to make the data collection more convenient online questionnaires for department heads and teachers were developed, and a link of the questionnaire was emailed through mailing address to the department heads and teachers of the selected universities. To analyze the collected data SPSS version, 22 was used. Data was analyzed by using mean and standard deviation for descriptive analysis. Chi-square association test was applied to examine the effect of leadership styles and team management on job satisfaction.
Results Demographic Profiles of Participants Table 2. Analysis of Demographic Variables of Respondents
|
Respondents’ Demographics |
Department Heads |
% |
Faculty Members |
% |
|
|
Gender |
Males |
29 |
72.50% |
147 |
84.00% |
|
Females |
11 |
27.50% |
28 |
16.00% |
|
|
Age Band |
Below
30 Years |
0 |
0% |
9 |
5.14% |
|
30-39
Years |
6 |
15.00% |
140 |
80.00% |
|
|
40-49
Years |
29 |
72.50% |
13 |
7.43% |
|
|
50
Years and Above |
5 |
12.50% |
13 |
7.43% |
|
|
Qualification |
M.A./M.Sc. |
0 |
0% |
6 |
3.43% |
|
M.Phil./M.S |
3 |
7.50% |
146 |
83.43% |
|
|
Ph.D. |
37 |
92.50% |
23 |
13.14% |
|
|
Faculty Rank |
Lecturer |
0% |
0% |
130 |
74.29% |
|
Assistant
Professor |
10 |
25.00% |
33 |
18.86% |
|
|
Associate
Professor |
14 |
35.00% |
10 |
5.71% |
|
|
Professor |
16 |
40.00% |
2 |
1.14% |
|
|
Professional Experience |
Less
than three years |
4 |
10.00% |
12 |
6.86% |
|
3-9
Years |
8 |
20.00% |
140 |
80.00% |
|
|
10
Years and Above |
28 |
70.00% |
23 |
11.43% |
|
|
Total |
40 |
100% |
175 |
100% |
|
Table 2
indicates about 72.50% were male and 27.50% were female. About 84% teachers
were male, and 16% were female. From age 30 to 39 years, there were 15.00%
heads, age band 40 to 49 years indicate 72.50% heads. About 12.50% heads were
related to the 50 years and above age. For ages below 30 years, there were
5.14% teachers. From age 30 to 39 years there were 80.00% teachers, whereas the
age band 40 to 49 years indicate that there were 7.43% teachers. Only 7.43% of
teachers were related to the 50 years and above age band category. About 7.50%
heads those were holding M.Phil. degree and 92.50% heads were Ph.D. degree.
About 3.43% of teachers hold M.A/M.Sc. Degree and currently enrolled in M.Phil.
degree, and 83.43% were holding M.Phil. degree and 13.14% teachers were Ph.D.
degree. About 25.00% of the head were assistant professors, 35.00% were
associate professors and 40.00% were designated as professors, it indicates
that about 74.29% of the teachers were lecturers, about 18.86% were assistant
professors, 5.71% were associate professors, and 1.14% were designated as
professors of social science departments. About 10.00% of the heads had less
than three years of experience as the head. About 20.00% had 3 to 9 years of
experience. About 70.00% had the experience of more than 10 years. About 6.86%
of the teachers were having less than three years of experience. About 80.00%
had 3 to 9 years of experience. About 11.43% had the experience of more than 10
years.
Association between Team Management
of University Heads and Job Satisfaction of University Teachers
Table 3. Association between Independent and Dependent Variables
|
Independent Factors of Heads’ Leadership Style |
No. of Teachers |
Dependent Factors of Teachers’ Job Satisfaction |
d.f |
Contingency Coefficient |
p-value |
?2 |
|
Autocratic (n=40)(x?=3.60)(?=1.03) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.4162 |
0.00001 |
36.667* |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.2474 |
0.0223 |
11.412* |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.4446 |
0.00001 |
43.103* |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.1869 |
0.1758 |
6.331 |
|||
|
Democratic (n=40)(x?=2.78)(?=0.49) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.4512 |
0.00001 |
44.725* |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.3067 |
0.0011 |
18.177* |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.4766 |
0.00001 |
51.421* |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.3313 |
0.00024 |
21.571* |
|||
|
Laissez-Faire (n=40)(x?=3.39)(?=1.03) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.1338 |
0.5267 |
3.189 |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.1098 |
0.7108 |
2.136 |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.4584 |
0.00001 |
46.561* |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.4498 |
0.00001 |
44.391* |
|||
|
Independent Factors of Heads’ Team Management |
No. of Teachers |
Dependent Factors of Teachers’ Job Satisfaction |
d.f |
Contingency Coefficient |
p-value |
?2 |
|
Creative Climate (n=40)(x?=3.74)(?=1.06) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.2492 |
0.0207 |
11.583* |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.3140 |
0.00074 |
19.145* |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.4089 |
0.00001 |
35.125* |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.4617 |
0.00001 |
47.415* |
|||
|
Problem Solving (n=40)(x?=3.25)(?=1.24) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.4207 |
0.00001 |
37.631* |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.2455 |
0.0242 |
11.220* |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.4707 |
0.00001 |
49.812* |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.4341 |
0.00001 |
40.627* |
|||
|
Goals and Standards (n=40)(x?=2.92)(?=1.13) |
175 |
Work |
4 |
0.4555 |
0.00001 |
45.826* |
|
Working
Conditions |
0.1321 |
0.5399 |
3.108 |
|||
|
Supervision |
0.1520 |
0.3873 |
4.141 |
|||
|
Promotion |
0.1748 |
0.2382 |
5.518 |
*p-value
< 0.05, Significant at p=0.00001,
Critical Region at 9.488
Table 3 also shows the ?2
value (11.583) indicates that there
exists an association between the creative climate of university heads and the
work of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.2492 indicates a weak
association. The p-value 0.0207 indicates
that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (19.145) indicates that there
exists an association between the creative climate of university heads and
working conditions of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.3140
indicates a weak association. The p-value of 0.00074 suggests that there is a statistically significant
relationship between factors. The ?2
value (35.125) indicates that there exists an association between creative
climate of university heads and supervision of university level teachers
contingency coefficient is 0.4089 indicates a strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a
statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (47.415) indicates that there
exists an association between the creative climate of university heads and
promotion of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4617 indicates
strong association. The p-value of
0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship
between factors. The ?2 value (37.631) indicates that there exists association
problem solving of university heads and work of university teachers contingency
coefficient is 0.4207 indicates strong association. The p-value of 0.00001 indicates that there is a
statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (11.220) indicates that there
exists an association between problem-solving of university heads and working
conditions of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.2455 indicates
weak association. The p-value of
0.0242 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship
between factors. The ?2
value (49.812) indicates that there
exists an association between problem solving of university heads and
supervision of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4707 indicates
strong association. The p-value of 0.00001
indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between
factors. The ?2
value (40.627) indicates that there
exists an association between problem-solving of university heads and promotion
of university-level teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4341 indicates strong
association. The p-value of 0.00001 indicates
that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (45.826) indicates that there
exists an association between goals and standards of university heads with work
of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4555 indicates strong
association.
The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a
statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (3.108) indicates that there is
no association between goals and standards of university heads with working
conditions of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.1321 indicates
no association. The p-value of 0.5399 indicates
that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (4.141) indicates that there is
no association between goals and standards of university heads with the
supervision of university teachers contingency coefficient 0.1520 indicates no
association. The p-value of 0.3873 indicates
that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between factors. The ?2
value (5.518) indicates that there is
no association between goals and standards of university heads with the
promotion of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.1748 indicates no
association. The p-value of 0.2382
indicates that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between
factors.
Association between Leadership Styles of University Heads and Job Satisfaction of University Teachers
Table 3 shows that the calculated ?2 value (36.667) is greater than the table value of chi-square, which is 9.488. It indicates that there exists an association between autocratic leadership style of university heads and work of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4162 indicates strong association. The p-value of 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (11.412) indicates that there exists an association between the autocratic leadership style of university heads and working condition of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.2474 indicates weak association. The p-value 0.0223 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (43.103) indicates that there exists an association between autocratic leadership style of university heads and supervision upon university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4446 indicates strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (6.331) indicates that there is no association between autocratic leadership style of university heads and promotion of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.1869 indicates no association. The p-value 0.1758 indicates that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (44.725) indicates that there exists an association between democratic leadership style of university heads and work of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4512 indicates strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (18.177) indicates that there exists an association between the democratic leadership style of university heads and working condition of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.3067 indicates weak association. The p-value 0.0011 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (51.421) indicates that there exists an association between democratic leadership style of university heads and supervision upon university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4766 indicates strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (21.571) indicates that there exists an association between democratic leadership style of university heads and promotion of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.3313 indicates moderate association. The p-value 0.00024 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (3.189) indicates that there exists no association between laissez-faire leadership style of university heads and work of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.1338 indicates no association. The p-value 0.5267 indicates that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (2.136) indicates that there is no association between laissez-faire leadership style of university heads and working condition of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.1098 indicates no association. The p-value 0.7108 indicates that there is a statistically non-significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (46.561) indicates that there exists an association between laissez-faire leadership style of university heads and supervision upon university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4584 indicates strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors. The ?2 value (44.391) indicates that there exists an association between laissez-faire leadership style of university heads and promotion of university teachers contingency coefficient is 0.4498 indicates strong association. The p-value 0.00001 indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between factors.
Analysis of Open-Ended Items Table 4. Leadership and team management challenges (Open-Ended Responses)
|
S. No |
Responses |
Respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Sense of purpose and contribution |
49 |
22.79% |
|
2 |
Follow organizational standards |
40 |
18.60% |
|
3 |
Decision Making |
28 |
13.02% |
|
4 |
Collaboration |
33 |
15.35% |
|
5 |
Appreciation |
18 |
8.37% |
|
6 |
Motivate Individual and Teams |
16 |
7.44% |
|
7 |
Improving system performance |
13 |
6.05% |
|
8 |
Team Communication |
9 |
4.19% |
|
9 |
Privacy Management |
5 |
2.33% |
|
10 |
Information Sharing |
4 |
1.86% |
|
Total |
215 |
100% |
|
Table 4
shows first challenge mentioned by the respondents was promoting a sense of
purpose and contribution (22.79%). The second challenge was to follow the
organizational standards (18.60%). Decision making (13.02%) is another high
rated challenge. Collaboration (15.35%) is also the significant challenge.
Appreciation (8.37%) is also a challenge for the heads and faculty members.
Motivation (7.44%) is also a challenge with reasonable rate. Improving the
performance (6.05%) is also the challenge for the department head.
Communication (4.19%) among team members is a challenge. Privacy (2.33%) of
departmental matters and issues is essential and a challenge. Sharing
information (1.86%) is also essential to promote the departmental achievements.
Table 5. Thematic Analysis of Interview Protocol
|
S. No |
Theme Observed (Skills of Leadership and Team
Management) |
Respondents |
Percentage |
|
1. |
Fair leadership, team management and effective
communication skills |
01 |
25% |
|
2. |
Collaboration skills and critical thinking |
01 |
25% |
|
3. |
Appropriate planning and self and staff management |
01 |
25% |
|
4. |
Problem solving skills and decision making skills |
01 |
25% |
|
Total |
04 |
100% |
|
|
S. No |
Theme Observed (Problems of Leadership and Team Management) |
Respondents |
Percentage |
|
1. |
Busy schedule of leaders |
01 |
25% |
|
2. |
Not enough time for motivation and getting feedback |
01 |
25% |
|
3. |
Workload |
01 |
25% |
|
4. |
Multiple administrative responsibilities |
01 |
25% |
|
Total |
04 |
100% |
|
|
S. No |
Theme Observed (Suggestions to Avoid Problems) |
Respondents |
Percentage |
|
1. |
Effective leadership and team management strategies |
01 |
25% |
|
2. |
Learning for experiences |
01 |
25% |
|
3. |
A compelling vision with self-motivation and
motivation of team heads |
01 |
25% |
|
4. |
Inspire others and be a true mentor |
01 |
25% |
|
Total |
04 |
100% |
|
Table 5 shows skills included fair leadership, team management and effective
communication skills (25%), collaboration skills and critical thinking (25%),
appropriate planning, self and staff management (25%), problem solving and
decision making skills (25%). Problems included busy schedules of deans (25%),
not having enough time to motivate and gaining feedback (25%). Deans are mostly
overloaded with duties (25%), and several administrative responsibilities
(25%). Suggestions to avoid problems of leadership and team management included
adopting effective leadership style and team management strategies (25%),
learning for experiences (25%), a compelling vision, motivating yourself and
team of heads (25%), and inspire others and be a true mentor (25%)
Discussion
The present study was conducted to explore the impact of leadership and team management practices of heads on the job satisfaction of faculty members at the university level. The present study results indicated association between independent and dependent variables. The present study also showed a strong significant effect of leadership and team management of heads on job satisfaction of the teachers at the university level.
Thematic analysis of interview provided skills of leadership and team management included fair leadership and team management strategies, effective communication skills, collaboration skills, critical thinking, appropriate planning, self-management, staff management, problem solving skills and decision making skills, these results verified the results of the study by Peterson (1997). He conducted a study on leadership styles and decision making. Problems of leadership and team management included busy schedules of deans and not having enough time to motivate heads and gain feedback from heads’ team. The results of present study are in line with the findings of Noureen, Shah and Zamir (2020) that heads used democratic leadership style. Workload of several administrative responsibilities, these results verified the results of the study by Armitage et al. (2006). They conducted a study on the relationship between team management and job satisfaction. Suggestions to avoid problems of leadership and team management included effective leadership and team management strategies, learning for experiences, a compelling vision, motivating yourself and team of heads, inspire others and be a true mentor, these results verified the results of the study by Watkins (2007). He conducted a study on leadership gaps.
The study was correlational in nature. Chi-square association test is used to deal with formulated hypotheses. The study rejected the null hypotheses related to categories autocratic and democratic styles that are strongly associated with job satisfaction levels as compare to laissez-faire style as the study accepted the null hypotheses related to this style and job satisfaction categories, these results verified the results of the study by Hulpia & Devos (2009), they conducted a study on the relationship between leadership and job satisfaction. The findings are also in line with Shah and Jumani (2017) that job satisfaction was the main factor of leadership styles. Exceptionally the study accepted null hypothesis related to autocratic style that is not associated with promotion of the employees. The study rejected the null hypotheses related to team management categories of heads creative climate, problem solving have strong association with factors of job satisfaction which include work, promotion, working condition and supervision as compare to goals and standard approach which is not associated with satisfaction level of employees as the study accepted the null hypotheses related to this category and job satisfaction categories, these results verified the results of the study by Littlejohn (1982). He conducted a study on the relationship between team management and job satisfaction. The study shows a strongly significant effect of team management of heads on job satisfaction of teachers. Furthermore, a research conducted Shah, Kashan and Nazir (2021) found that leadership competencies also effect the job satisfaction of the employees.
The discussion of the study concludes that selecting an appropriate leadership style and the team management approaches could lead the educational institutions to achievement of desired goals and job satisfaction of the faculty members. Statistical data analysis indicated mixed results with most variables showed a positive significant association with each other.
Conclusions
1. The study concluded that the most frequently used leadership styles were autocratic, democratic and laissez-faire styles and team management competencies involved creative climate, problem solving, and goals based on institutional standards.
2. The study concluded that competency areas of teachers’ job satisfaction involved work, working conditions, supervision and promotion.
3. The present study concluded that the leadership style of heads had a great effect on job satisfaction and there was a strong association between heads' leadership style with job satisfaction of teachers. Autocratic and democratic styles are strongly associated with job satisfaction levels as compared to laissez-faire style. Exceptionally autocratic style is not associated with promotion of the employees. The present study also concluded that team management of heads creative climate, problem solving have strong association with factors of job satisfaction which include work, promotion, working condition, supervision as compare to goals and standard approach which is not associated with satisfaction level of employees. So there is a relationship exists between team management of head and job satisfaction of faculty members.
4. The present study concluded that on ground leadership and team management competency challenges include sense of purpose and contribution, following the organizational standards, decision making, collaboration, appreciation and team motivation, improving system performance, team communication, privacy, sharing information.
5. Thematic analysis of the interview concluded that skills of leadership and team management include fair leadership and team management strategies, effective communication skills, collaboration skills, critical thinking, appropriate planning, self-management, staff management, problem solving skills and decision making skills. Problems of leadership and team management include busy schedules of deans and not having enough time to motivate heads and gain feedback from heads' team. Workload of several administrative responsibilities. Suggestions to avoid problems of leadership and team management included effective leadership and team management strategies, learning for experiences, a compelling vision, motivating yourself and team of heads, inspire others and be a true mentor.
Recommendations
1. Leadership strategies could also be integrated to the existing leadership approaches such as transactional, transformational and servant leadership. Other team management strategies could also integrated such as communication, productivity consciousness, participative climate, interpersonal climate and motivation to test effect of these additional strategies to job satisfaction variable.
2. Other job satisfaction factors may also be used as dependent variables such as salary and workgroups.
3. Null hypothesis related to laissez-faire style of leadership variable were accepted in which indicated no association with job satisfaction, future studies may assess the association by using other styles such as transactional leadership, transformational leadership and servant leadership. Null hypothesis related to goals and standards category of team management variable were accepted which indicated no association with job satisfaction, future studies may assess the association by using other team management categories such as communication, productivity consciousness, participative climate, interpersonal climate and motivation.
4. Provision be made for heads to upgrade their training in educational leadership and educational team management to avoid the on ground leadership and team management challenges being faced by both heads and teachers.
5. Heads should know the levels of learning in their departments, job satisfaction level, and ability to share leadership and team management tasks with faculty members so that maximum results from the academic process would be achieved.
6. Higher education institutions and admin staff investigate alternatives with the intention of making programs more relevant to the needs of heads and faculty members.
7. Heads may facilitate and manage the mechanism to effectively use leadership and team management strategies to enhance the job satisfaction of teachers which could ultimately result in the academic achievement of learners.
8. Heads must be equipped with effective communication skills to effectively convey departmental values and standards to subordinates.
9. FDP (Faculty Development Program) must integrate leadership and team management skills for heads of departments in each academic sector to avail advantages of leadership and team management strategies.
References
- Armitage, J. W., Brooks, N. A., Carlen, M. C., & Schulz, S. P. (2006). Remodeling leadership: developing mature leaders and organizational leadership systems (an introduction to the Leadership Maturity Model™). Performance Improvement, 45(2), 40-47. doi:10.1002/pfi.2006.4930450208
- Bateman, T. S., & Snell, S. A. (2002). Management: Competing in a new era. New York: McGraw- Hill
- Bennis, W., & Nanus, B. (1985). Leader: The Strategies for Taking Charge, New York: Harper and Row.
- Casimir, G. (2001). Combinative aspects of leadership style: The ordering and temporal spacing of leadership behaviors. The Leadership Quarterly, 12(3), 245-278.
- Gay, L. R., & Airasian, P. W. (2000). Educational research: Competencies for analysis and applications. Boston: Pearson.
- Green, J. (2000). Job satisfaction of community college chairpersons. Doctoral Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic and State University, Blacksburg, VA.
- Grundy, W., & Blandford, S. (1999). Developing a culture for positive behaviour management. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 4(3), 5- 9.
- House, R., Javidan, M., Hanges, P., & Dorfman, P. (2002). Understanding cultures and implicit leadership theories across the globe: an introduction to project GLOBE. Journal of world business, 37(1), 3-10.
- Halpin, H., & Devos, G. (2009). Exploring the link between distributed leadership and job satisfaction of school leaders. Educational Studies, 35(2), 153-171.
- Jennings, A. T. (2000). Hiring generation- X. Journal of Accountancy, 189(2), 55-59.
- Khanka, S. S. (2002). Organisational Behaviour. Finance India, 16(1), 329- 329.
- Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and psychological measurement, 30(3), 607-610.
- Kunwar, F. (2001). School Leadership and School Effectiveness: Reflections and Research in the context of Pakistan. Lahore: Nawa Publications.
- Lawler, E. E. (1973). Motivation in Work Organization. Brooks/Cole, Monterey, California
- Littlejohn, R. F. (1982). Team Management: A How-to Approach to Improved Productivity, Higher Morale, and Longer-Lasting Job Satisfaction. Management Review, 6(3), 23-28.
- Lunenburg, F. C., & Ornstein, A. C. (2011). Educational administration: Concepts and practices. Cengage Learning.
- Margerison, C. J., & McCann, D. (1990). Team management: Practical new approaches. Chaldford: Management Books 2000 Ltd.
- Martinez-Pons, M. (1990). Test of a Three- Factor Model of Teacher Commitment.
- McShane, S. L., & Glinow, M. A. V. (2004). Organizational behavior. New York: McGraw- Hill.
- Green. M., Shah, N. H., & Zamir, S. (2020). Effect of Leadership Styles of Secondary School Heads on School Improvement. Global Social Sciences Review, 5(1), 519-527.
- Owens, R. G. (1987). Organizational behaviour in education. 3rd ed. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
- Peterson, R. S. (1997). A directive leadership style in group decision making can be both virtue and vice: Evidence from elite and experimental groups. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72(5), 1107-1117.
- Reece, B. L., & Brandt, R. (1999). Effective human relations in organizations. Houghton Mifflin College Division.
- Sergiovanni, T. J., & Starratt, R. J. (1979). Supervision: Human perspectives. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Shah, N. H., & Jumani, N. B. (2015). Relationship of Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention of Private Secondary School Teachers. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(4), S2, 313-323.
- Shah, N. H., Kashan, S., & Nazir, N. (2021). Leadership Competencies: A Study of In-service Training of School Teachers. Pakistan Journal of Educational Research, 4(1), 178-197.
- Sweeney, P. B., & McFarlin, D. B. (2012).
- Swift, J. S. (1971). The Origins of Team Management. National Elementary Principal, 50(4), 26-35.
- Watkins, M. (2007). How to fill the leadership gap. Directorship, 33, 22- 24.
- Wu, M. Y. (2006). Compare participative leadership theories in three cultures. China Media Research, 2(3), 19-30.
- Zembylas, M., & Papanastasiou, E. (2006). Sources of teacher job satisfaction and dissatisfaction in Cyprus. Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, 36(2), 229-247.
Cite this article
-
APA : Shah, N. H., Shaheen, S., & Asghar, S. (2021). Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level. Global Economics Review, VI(II), 173 - 188. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2021(VI-II).14
-
CHICAGO : Shah, Nazir Haider, Shabeena Shaheen, and Saima Asghar. 2021. "Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level." Global Economics Review, VI (II): 173 - 188 doi: 10.31703/ger.2021(VI-II).14
-
HARVARD : SHAH, N. H., SHAHEEN, S. & ASGHAR, S. 2021. Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level. Global Economics Review, VI, 173 - 188.
-
MHRA : Shah, Nazir Haider, Shabeena Shaheen, and Saima Asghar. 2021. "Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level." Global Economics Review, VI: 173 - 188
-
MLA : Shah, Nazir Haider, Shabeena Shaheen, and Saima Asghar. "Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level." Global Economics Review, VI.II (2021): 173 - 188 Print.
-
OXFORD : Shah, Nazir Haider, Shaheen, Shabeena, and Asghar, Saima (2021), "Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level", Global Economics Review, VI (II), 173 - 188
-
TURABIAN : Shah, Nazir Haider, Shabeena Shaheen, and Saima Asghar. "Impact of Heads' Leadership and Team Management Competencies on Teachers' Job Satisfaction at University Level." Global Economics Review VI, no. II (2021): 173 - 188. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2021(VI-II).14
