Abstract:
China's peaceful ascent has had a significant impact on the global economic system. There are two major reasons for this: the first and most important is Beijing's peaceful expansionist policies, and the second is its advanced industries and technologies. Their goal is to dominate global raw materials as well as the market through their goods. China has been working hard to promote built-and-road policies around the world in order to attain these aims, but it is also confronting various intra- and inter-level possibilities and obstacles. The purpose of this article is to analyse the Built-Road and the Sino-Pak economic corridor in general, as well as the obstacles and prospects for China's Xinjiang province in particular. Xinjiang's ambitious economic development plan calls for more than $8 billion in spending over the next five years alone. Its goal is to fully integrate Xinjiang into China's booming economy and absorb its people as equal citizens of the multi-ethnic state ruled by Beijing.
Key Words:
Sophisticated, Expansionism, Socio-Economic Development, Xinjiang,
Burgeoning
Introduction
The bulk of the people of Xinjiang lives in poverty, making it one of China's undeveloped provinces. Different challenges have arisen in Xinjiang as a result of tensions between the Hans and the ethnic Muslim Uyghur. The economic structure, natural resources, and external influences are all factors that contribute to these difficulties. To address the challenges in Xinjiang, the Chinese government has implemented a variety of socioeconomic measures. The socioeconomic situation in Xinjiang has a significant impact on their society's ethnic structure since several evidence suggest that the Xinjiang conflict is mostly caused by low socioeconomic conditions. Socioeconomic disparities between ethnic groups have bred a climate of violence and terrorism, posing a serious threat to China's safe keeping and commercial solidity. By means of a result, the Chinese dominant administration has taken various socioeconomic initiatives to handle the Xinjiang situation. Xinjiang's economic and social development may be traced back to the Qing Dynasty. When Xinjiang was recognised as a province of the Chinese empire in 1884, the Qing Dynasty began on an aggressive economic expansion strategy. Agriculture began to be commercialised, and other aspects of the economy, including as handicrafts, coal and oil extraction with Russian assistance, and an increase in foreign trade, all profited from the British-Russian royally competition in Central Asia (Cohen, 2013). The political and social chaos that followed the collapse of the Qing Dynasty in 1911 had a negative impact on Xinjiang's economy (Cheng, 1989). Agricultural development was prioritised during Yang Zengxin's reign, and Xinjiang exported agricultural goods and imported industrial goods, but Jin Shuren's corrupt leadership stifled the region's progress. Sheng Shicai, with the help of the Soviet Union and liberal reforms, brought Xinjiang's economy back to life in 1938. (Cohen, 2013). The impact of China's civil war and in the time of Second World War on Xinjiang's socioeconomic situation has deteriorated once more. The present CPEC and Built and Road initiatives provide another excellent opportunity to rebuild China's socioeconomic standing in this region.
Chinese political policies in Xinjiang
The explanation of the People's Republic of China's policies in Xinjiang can be divided into distinct time periods and Chinese leaders' government structures.
Source: The Economist
Mao Policies in Xinjiang
Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the Chinese communist party was successful in establishing the PRC in October 1949. In the Civil War, which had been raging for the previous twenty years, was likewise under the control of the CCP at the time. The ethnic diversity of Xinjiang, as well as Uyghur separatist activities, posed a challenge to the fledgling nation. Because of Uyghur and non-ethnic Han revolts and violence against the central government, Xinjiang became an independent region in 1944. However, when China became a Republic in 1949, Xinjiang was occupied by the People's Liberation Army, and Chinese central authorities and policymakers took various socioeconomic and political initiatives to control the Xinjiang conflict and uprising (Mackerras, 2002).
Demographic and Economic Structure
The demographic and economic relativity is important for states developments because increase in population has great impact on economic developments. In Xinxiang the below graph shown the correlations between population and economic structure.
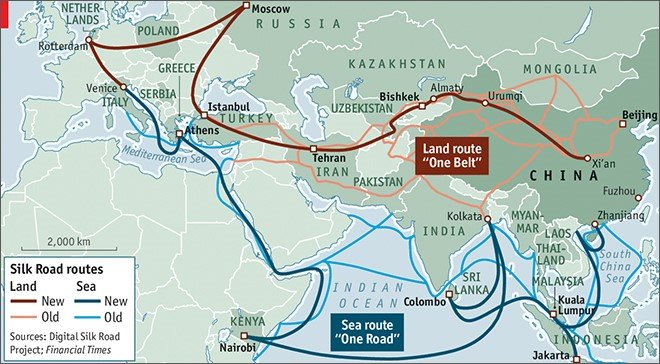
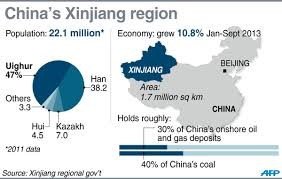
The CCP established the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in October 1955, but that autonomy does not imply that Xinjiang is an independent state; it must remain under Beijing's control. Through the programmers of the China Islamic Association, the Communist Party of China establishes close ties between Beijing officials and Uighur elites that control socioeconomic and holy authority (Dillon, 1997). Because these districts were highly populated with separatist and extremist Uyghurs, the CCP adopted this policy to counter such movements as well as border threats. Production and construction corps units were also formed in Uyghur majority areas including as Kashgar, Ahsu, and Qumal. The rationale behind this programme is to assist Han and other non-Uyghur ethnic groups because if a Uyghur revolt for independence occurs in the future, all other minorities will band together with Han Chinese to combat Uyghur nationalist activities (Dani, 2014).
From 1976 through 1990, China's policy in Xinjiang were shaped by Mao Zedong.
The end of the Cultural Revolution and Mao Zedong's death in 1976 result in a profound shift in policymakers' and Chinese authorities' minds. The Xinjiang Uyghur minority's socioeconomic position, as well as their culture and identity, have been stabbed by the Cultural Revolution and hard policies, and as a result, Chinese policymakers have realized that maintaining these rigid rules will exacerbate the subgroups' hitches, As a result, in Xinjiang, they have undertaken changes in the form of forced political tightening. Coercive political and economic practices are still at the root of the Uighur-Han conflict in China today (Madsen R. , 2009).
Once Deng Xiaoping became the leader of the PRC in 1978, he implemented some significant improvements in socio-political, and socio-economic policies that were more favourable to Xinjiang's socioeconomic situation, as well as Uyghur freedom of expression and intellectual expulsion. The intellectuals of the Uyghur people want to express themselves through books, papers, and essays, as well as reveal their past reminiscences. As a result of these writings and historical recollections, Uyghur minorities are reminded that Xinjiang was once an independent Uyghur region (Millward, 2006). Because of the recording and sharing of history, the Uyghur ethnic minority became united in their desire for an independent state, and they began protesting and destroying property in various parts of Xinjiang. Because Beijing is concerned about Uyghur terrorist operations, it has banned a variety of illegal books, leaflets, and publications, causing divisions among ethnic groupings as well as Uyghur independence movements (Nicolas, 2000). To regulate the population of Uyghur minorities in rural and urban areas in Xinjiang, the Youhui Zhengce family planning system was devised. The national family planning programme allowed one child per home in urban areas and three children per household in rural areas, however the Uyghur cannot accept this policy, which they regard as eliminating Non Han minority households (Cohen, 2013). In addition to education, infrastructure, and employment, the Chinese central government sponsored various social development strategies in Xinjiang's primarily Uyghur-populated cities. Even though the majority of non-Han people were chosen to government jobs, some ethnic minorities felt oppressed by Han supremacy in government positions (Mackerras, 2002).
The Shanghai Five and Xinjiang
The Soviet Union fell apart in the 1990s, and the newly independent Central Asian governments gained independence. This momentous episode causes distinct changes in China's policies toward Xinjiang because it alleviates China's worry of Soviet influence in the region, but it also raises concerns in Beijing about the reason to deal with the new independent country. Because the fresh autonomous republics and their societies share a close societal and racial bond with Xinjiang's Muslim Uighur populations. In 1996, the Chinese governments formed the Shanghai Five, which included Russia, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and was later renamed the Shanghai Cooperation Organization with the addition of Uzbekistan in 2001. The major goal of this organisation is to combat Uyghur militancy and religious extremism with the help of member states (Hyer E. , 2006).
Chinese Societal Policies inside Xinjiang
The immovability of Xinjiang is critical for China's economic and passive development, since any instability in that region has a direct impact on the country's sociopolitical and economic climate. When Xinjiang terrorist attacks occurred in Urumqi, the capital of the autonomous province of Xinjiang, in 2009, to stabilize Xinjiang and secure central China, the Chinese Communist Party created a number of strategies to counter these separatist and destructive forces (N, 2014). To combat terrorism, the strike hard strategy has been enforced, as have limitations on religious activity, particularly for Uyghur Muslims. In order to achieve the goal of socioeconomic unification and homogeneity in Xinjiang, the Bilingual Education Policy was implemented in order to teach ethnic minorities and their children in Chinese. Another significant tactic adopted by the communist party to alter the Chinese population in Xinjiang and reduce the number of Uyghurs was the Han migration scheme. Because the problem persists among numerous populations, several researchers and organisations have questioned these tactics on a variety of reasons. Inside China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, the Uyghur face deprivation in various aspects of their lives as a result of Han dominance policies (Jamil, 2011).
Economic Growth of Xinjiang
Uyghur racial mainstream and underdevelopment in Xinjiang pose a severe threat to Chinese sovereignty. The Chinese government pushes a variety of initiatives to address the problem, but the majority of them are divisive, raising new concerns every day. Because the majority of Uyghurs living in slandered are poor, the Uyghur-Han conflict is primarily about economic discrimination and relative deprivation. The Chinese government's first and most important goal is to grow Xinjiang, with a particular focus on Uyghur-majority districts, in order to resolve the dispute between major ethnic groups over economic hardship and the Uyghur insurrection (S, 2014).
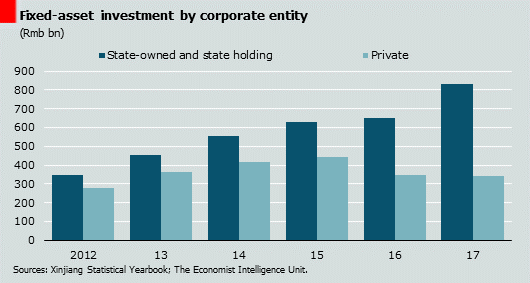
The instability in Urumqi, the capital of Xinjiang, in the 1990s pushed Beijing to implement developmental programmes in the region. Because policymakers understand that economic development may transform the Uyghur people's traditional way of life into a contemporary one, avoiding disputes and bringing stability to Xinjiang (Dani, 2014).
The Great Western Development (GWD)
The fundamental goal of Beijing's agendas was to develop China's western flank. The Great Western Development package encompasses a variety of topics and initiatives. These programs primarily targeted China's socioeconomically disadvantaged districts and provinces, with the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, being one of the greatest pressing problems. The fundamental goal of this programmed was to advance the economy and living values of Hanseatic people through developing infrastructure, transportation, roads, rail lines, energy, communication, outside investment, education, and immigration (Widyastuti, 2013).
Education Policies inside Xinjiang
Because it is China's education policy that studying is a fundamental right of Chinese students, the country has the most schools in the world. However, ethnic diversity within China, particularly in Xinjiang, can provide challenges for policymakers. The ethnic situation in Xinjiang between Han and Uyghur is exploitative, and it has an impact on the educational system (Yusuf, 2020). In Xinjiang, there are three types of school systems in operation: Han school system, where the majority of students and teachers are ethnic Han; Han school system, where the majority of students and teachers are ethnic Han; and Han school system, where the majority of students and teachers are ethnic Han. Due to language differences between ethnic groups, the second is a combined school system, in which students from diverse ethnic groups study together, and the third is an ethnic school system, which is dominated by students from minorities. The Chinese government has launched a number of educational projects in Uyghur-majority areas with the goal of educating Uyghurs and other minorities (Cohen, 2013). The national education policy of bilingual education has made a significant contribution to Xinjiang's educational progress. Minorities taught their mother tongue as well as the national language, Mandarin, at school under this educational program. Before the Xinjiang educationists' new bilingual education policy in 2002, the mother tongue was employed as the medium of instruction, and national language was a difficult subject for minorities to learn. Mandarin was employed as the medium of instruction in courses once the new bilingual policy was implemented, and mother tongue was added to the curriculum as a subject, (Razvan, 2005). Several international nongovernmental organisation (INGO) programmes are also striving to enhance education in Xinjiang, with Save the Children being one of the most major INGO projects working under China's national education plan in the region. With these restrictions, the Chinese government hopes to promote high-quality education for ethnic minorities while preventing educational gaps between ethnic Uyghurs and Han Chinese. (Cheng, 1989).
Religious Strategies
Taoism, Islam, Buddhism, Catholics, and Protestants are the five official religions practised by the Chinese people. Confucianism, Buddhism, and the national religion Taoism, in addition to these religious differences, play important roles in the moral lives of Chinese people. Only Taoism was the main religion of the Chinese before to independence, and other religions were introduced to Chinese communities at various times throughout history (Madsen R. , 2010). It was a long-held Chinese belief that politics and religion are inextricably linked. Religion is crucial in the Xinjiang conflict between Han and Uyghur. Because the Uyghur, are Sunni Muslims and the Han are Buddhists, these theological changes contribute to the ethnic conflict in China's Xinjiang region, as well as causing problems for Beijing policymakers. The intimate relationships between Uyghurs and the Muslim Ummah, as well as some extreme groups, are changing the socio-political landscape in Xinjiang (AFP, 2019).
Muslims in China were allowed to freely safeguard their culture and identity throughout Deng's reign, as well as engage in religious activities such as fasting during Ramadan, Haj, Namaz, preaching Islam, and Zakat, among others. At the time, the Chinese government implemented several developmental initiatives in Xinjiang, including road infrastructure, industries, and schools, and it was a period when the Muslims in Xinjiang remained strongly linked to the Muslim sphere, particularly of Pakistan and Saudi Arabia, along with Afghanistan (Jamal, 2011). Because they receive money from various Muslim states and utilise it to develop Masjed and Madrasas as well as deliver religious materials (Quran) to schools, Xinjiang's Muslim ties with the Muslim Ummah boost the Uyghur Muslim position in China even more. These ties and support have made the Uyghur people powerful, as well as politicised Islam in Xinjiang, which supports Uyghur separatist activities (Hyer E. , 2006). Unrest in Xinjiang by Uyghurs in 1990, as well as other damaging operations by Uyghur terrorists, forced Beijing to adopt repressive religious, policies. Islamic militants and Xinjiang Muslim activists' ties to worldwide extremist groups, according to several experts, researchers, and Chinese officials, play a larger role in the uprising in Xinjiang (Dani, 2014). Since the 1980s, according to Yitzhak Shichor, the Chinese government has lost control over Uyghur religious activity (SHICHOR, 2005). Beijing employs a variety of incentives, including religious restrictive policies, to deter Uyghur Muslim extremism and terrorism within China. However, these religious policies have failed because Xinjiang is home to approximately 62 percent Muslims, and Islam plays a significant role in shaping their distinct and distinct identity from Han Chinese. China's religious, policies toward Muslims in Xinjiang have presented Beijing with new issues, as Beijing imposes restrictions on Islamic principles and conduct within Xinjiang (Zakria, 2020).
Containment of Terrorism and Separatism
For Xinjiang Muslims, the most serious issue was China's restrictive religious policies during Ramadan. Muslims cannot compromise on Islamic principles, not only in China's Xinjiang, but throughout the world. In the instance of Xinjiang, the Chinese government prohibits Muslims from fasting during Ramadan, which is unethical in the eyes of Chinese Muslim communities. The month of Ramadan, as well as religious events throughout that month, are extremely important in the lives of Muslims. For many years, restrictive religious laws and bans on Muslim religious activities such as fasting, seminars, preaching, pilgrimage, and so on were in place (Dani, 2014).
Beijing maintains that religious restrictions on Muslim Uyghurs and other ethnic groups in Xinjiang help to prevent separatism and terrorism, however such policies have failed to fulfil Beijing's goal because violence has escalated and separatist movements have become more active than before the rules. Following the implementation of these policies, news agencies reported attacks and uprisings from Uyghur Muslim sides in the month of Ramadan, in which over a hundred people were killed and injured, including imams from various Masjids, all because they were supporters of Chinese authority and their policies (Zakria, 2020). Terrorists and Uyghur separatists have been more active as a result of China's stringent religious policies, and they have acquired support from the Muslim world, particularly in Pakistan's tribal areas and Central Asia, where Uyghur Muslim separatist organisations are supported. Outside of China, religious extremists have intimate relations to religious extremists in Xinjiang, and this link is exceedingly dangerous for Chinese interests outside of China (Cheng, 1989). The Muslims along with Islamic religious movements were not a single the source of instability and discontent, but globalisation also had a role in the rise of the Uyghur issue, since information and technical advancements linked Uyghurs all over the world to the same goal (Madsen R. , 2010). The Chinese government's inequitable policies favour Han people over Uyghur Muslims un various aspects of life, such as jobs, education, health, and other socioeconomic activities, and they are also treated as second-class inhabitants.
Inter and Intra Migration Activities and economic Discrimination
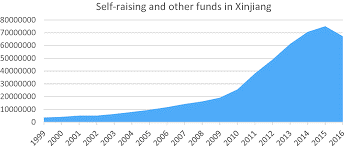
Xinjiang is one of China's major autonomous areas, with the potential to alleviate the country's overpopulation problem. The land gains a variety of natural resources, including oil, gas, and valuable stone mountains. The population of this particular land is small and heterogeneous, with more than 46 ethnic groups (Farhad, 2015). The largest ethnic groups are the Uyghur and Han, who have had a lengthy rivalry for many years. Since the 1990s, the Uyghur had been considered the majority in Xinjiang, however following terrorist acts and separatist movements by Uyghurs, the majority of Uyghurs have been reduced through various economic development and inter migration programmes (Wei, 2010). The Chinese government has never made any concessions in the Xinjiang case, which the Uyghurs desire to secede from China. Different economic policies are promoted by the Chinese government to develop Xinjiang, yet these policies are closely linked to Uyghur deprivation from Han. In 1940, seventy percent of the population of Xinjiang was Uyghur, ten percent Han, and twenty percent various ethnic minorities (Xiaogang Wu, 2013). Following the detention of the CCP in the 1940s, the PRC increased its influence in terms of military and developmental projects in the Uyghur Autonomous Region between 1956 and 1962, resulting in drastic changes in Uyghur position. The majority of Han relocated to Xinjiang and rose through the ranks of government and business in the province; such migration and the holding of high-ranking positions in various private and government institutions by Han posed a significant challenge to Uyghur separatist goals (Zakria, 2020). The Chinese government's development strategies in Xinjiang also entice Han industrialists and businessmen to set up businesses and spend their money, causing Han to flock to the region. By 1979, Chinese authorities' development initiatives had increased the Han population by 40% (Xiaogang Wu, 2013). As a result, Han internal immigration can directly help China's Xinjiang problem, because Uyghur minorities suffer deprivation as a result of Han migration on several social, political, and economic levels (Wavgh, 1-4). Many scholars and philosophers believe that economic underdevelopment is to blame for the conflict between Uyghur and Han in Xinjiang, but that unregulated internal migration of Han Chinese to Uyghur majority areas has also contributed to rising tensions between Chinese authorities and minorities. The development programmes and projects will assist Uyghurs in improving their level of living, but they will also encourage high-class Han to invest in Xinjiang, posing a threat to the Uyghur goal in China. Because the majority of Han migrants are well educated and skilled in a variety of technical fields, they are able to find lucrative professions and develop many forums and companies (Sebastian, 2008). Since the PRC's independence in 1949, the migration of Han Chinese to Xinjiang has been part of China's counter-Uyghur separatist policy. According to prominent Uyghur activist Rabia kadeer, the Chinese government is to blame for the Xinjiang problem since Beijing supports Han migration to Xinjiang, which weakens Uyghur political power and lowers Uyghur socioeconomic status. According to a recent survey, Han Chinese account for 44% of the population in Xinjiang, while Uyghurs account for 46% (Yusuf, 2020). For some years, the population gap between the two ethnic groups has been very narrow, and it is projected that if such movement of Han Chinese does not stop in the future, it will disrupt the Uyghur majority and socioeconomic status, causing perpetual friction between the two ethnic groups (Farhad, 2015).
Internal Han Chinese immigration has exacerbated socioeconomic and political inequities in Xinjiang, as the majority of ethnic Han people profit more from local resources than Uyghur ethnic groups. Not only was underdevelopment a problem in the Uyghur Autonomous Region of China, but so were Han migrants, who dominated their socioeconomic and political position above other non-Han racial sectors groups, and this hegemonic situation of Han Chinese affected a slew of other issues such as joblessness, radicalism, and edification for Uyghur Muslims (Zenn, 2018). The Chinese Authority established the Xinjiang Manufacture and Structure Corps in 1953-54 with the goal of developing infrastructure and the agriculture sector in rural areas. The unit was primarily founded by paramilitaries, and the majority of its members are now retired People's Liberation Army soldiers (Nicolas, 2000), and maximum of these army males were Han Chinese. Different unreasonable governmental actions caused the Han migration to Xinjiang and inequities among minorities. The influx of Han Chinese to Xinjiang dates back to 1949, as does the Uyghur revolt in Xinjiang's capital in 1990. The CCP has aided Han migration to Xinjiang province in order to establish a Han majority amid non-Han populations, enhance political power, and suppress Uyghur activists (Debasish, 2005).The majority of Han Chinese migrants to Xinjiang were migrating there for their own gain, and the west's migration reform policies and economic progress encouraged more Han individuals to live in Xinjiang. The migration of Han migrants into Xinjiang has been increasing steadily over the last few years, with the majority of them being labourers who migrate to places with government projects and enterprises (Gardner, 2004). The goal of these migrants is to enhance their standard of life and increase their gross, but on the other hand, unregulated Han Chinese self-migration causes inequities between rural and urban areas on the one hand, and between Uyghur and Han on the other (Gardner, 2004). The unbalanced migration to Xinjiang increases the overall population of the land; the graph shows that from 1948 to 2008, the population of Xinjiang increased dramatically from 3.6 million to 20.9 million, and when compared to the overall population growth of China, this is a significant rise (Cohen, 2013). As a result, the entire population of China grows at 1.5 percent each year, but the population of Xinjiang grows at 2.7 percent, which is extremely high and has an impact on the natural resources of this region (Debasish, 2005). China's latest development initiatives in Xinjiang point in the direction of the West. The Chinese government has established several economic zones and industrial sites, as well as making Xinjiang's capital a worldwide trade Centre, In two aspects, however, this investment has created an imbalance between Han and Uyghur. It causes tensions between rural and urban migration, as well as economic disparities among minorities, particularly between the Uyghur and Han ethnic groups (Graham E. Fuller, 2003). Han Chinese from all over China flock to Urumqi and other province cities because of such development schemes. These migrants take advantage of natural resources for their own gain rather than on an equal footing, and these disparities set Non Han Chinese against Han Chinese (Gardner, 2004).
From Migration to Deprivation Table 1.
|
Time |
Xinjiang overall Population |
Ethnic Uyghur Residents |
Migrants Han |
Other Migrants |
|
1945 |
4.28 |
3.20 |
0.25 |
0.83 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
74.76 |
5.84 |
19.39 |
|
1952 |
4.94 |
3.62 |
0.37 |
0.97 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
73.23 |
7.31 |
19.48 |
|
1965 |
7.39 |
4.00 |
2.38 |
0.98 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
55.22 |
32.38 |
13.41 |
|
1984 |
12.43 |
5.94 |
4.99 |
1.56 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
47.66 |
39.93 |
12.39 |
|
1991 |
14.3 |
7.00 |
5.00 |
2.3 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
49.28 |
35.22 |
15.49 |
|
1998 |
15.99 |
7.97 |
5.63 |
2.5 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
49.82 |
35,17 |
15.1 |
|
2005 |
18.29 |
8.25 |
7.22 |
2.9 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
45.07 |
39.44 |
15.32 |
|
2009 |
20.34 |
9.60 |
8.00 |
2.75 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
47.19 |
39.88 |
13.48 |
|
2015 |
23.3 |
11.15 |
10.98 |
2.9 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
47 |
46 |
16 |
|
2019 |
25.8 |
12.19 |
11.9 |
3.0 |
|
Ratio |
100 |
48 |
47 |
18 |
The absolute majority of Uyghur Muslims
has decreased since 1945, according to the above statistic, which illustrates
continued migration of Han Chinese to Xinjiang from 1945 to 2016. From 1950 to
1970, China's internal migration policy was relatively flexible, because the
country was more active in developing the west of the country, which resulted
in more jobs in the public and private sectors (Debasish,
2005). As a result, Han people are better educated and skilled than
Uyghurs and other non-Han Chinese, which is why Han people have been given more
opportunities to move to Xinjiang and hold higher positions in government and
private institutions than Uyghurs and other non-Han Chinese. These individuals
moved to Xinjiang for a multiplicity of causes, counting government policy and
self-interest (Shichor,
2005). According to Uyghur political
and social media personalities, Beijing is to blame for all issues in Xinjiang
because Beijing does not want Xinjiang to become an independent Uyghur state,
which is why it is developing the region without Uyghurs. Because Han Chinese
migration increases job market competition, Uyghurs continue to be marginalised
by Han Chinese. This type of rivalry has been going on for several years, not
just in the job market but also in other areas and sectors such as education,
agriculture, the military, and the social sector (Nicolas,
2000). The question arises as to whether the Han or the Uyghur will
win this competition. The reason is obvious: Han Chinese are well-trained,
educated, and skilled, and they have tight ties to government officials, as
well as direct and indirect backing from the Chinese government. As a result of
this competition and the Han Chinese's dominant role in Xinjiang, disparities
arise among both ethnic groups, forcing Non Han Chinese, particularly Uyghurs,
to turn against not only Han but also Beijing (S, 2014).
Ethnic composition in different governmental and private sector in Xinjiang Table 2.
|
Sectors |
Average |
Percentage of Ethnic Uyghur |
Percentage of ethnic Han |
|
Edifice
and Production |
25421 |
6.89 |
91 |
|
Energy,
oil and Gas |
40357 |
20.34 |
80.46 |
|
Government
Institution |
33232 |
29.97 |
58.46 |
|
Finance
and account |
55433 |
12.67 |
79.23 |
|
Edification
and ethnicity |
28745 |
36.13 |
43.34 |
|
Science
and Research |
34564 |
92.45 |
13.99 |
|
Agriculture
|
17834 |
48.34 |
28.17 |
|
Excavation
and Mining |
52144 |
81.43 |
15.75 |
|
Transport
sector |
43647 |
69.85 |
17.76 |
The figures in the table above support the positions of two ethnic groups: the Han ethnic group has a prominent role in Xinjiang's various resources, while the Uyghur ethnic group, on the other hand, and is excluded from the Han-dominated system's atmosphere and structure. Inequities between minorities are created as a result of Han migration to Uyghur majority areas, and these inequalities lead to violence and terrorism (Fan, 2009).
Conclusion
In the conflict between Ethnic Han and Ethnic Non Han, Beijing's socioeconomic policies for the Uyghur Autonomous Region play a crucial role. According to Chinese policymakers, such measures improve the socioeconomic status of minorities and help them develop their personalities through education, health care, and infrastructure. In twenty-first-century society, religion and economics are extremely important. Muslims all around the world cannot compromise on Islamic beliefs, even if they are poor and in the minority. In China's Xinjiang region, the Uyghur ethnic minority is also Muslim and poor, and these two aspects of their lives distinguish them from Han Chinese people in a variety of socio-political ways. Uyghur have been fighting for a separate state for some years, but the Chinese government has refused to negotiate with them on this goal, and Beijing has used various tactics to try to prevent peaceful Uyghur pro-independence rallies. However, the current socio-economic measures supported by the Chinese government to discourage minorities separatist movements and violence have created a commercial vacuum in Xinjiang, which is a potential opportunity for the province. The Uyghur in Xinjiang, as well as the rest of China, cannot tolerate Han supremacy over social, political, and economic institutions, yet Han hegemony in the Uyghur Autonomy Region is maintained through unrestricted internal migration of Han to Xinjiang. As a result, the CPEC, together with its built and road policies, has had a significant impact on this region, and in the not-too-distant future, this project will alleviate all of Xinxiang's difficulties.
References
- AFP. (2019, may wensday). Xinjiang Crackdown on Ethnic Minorities at the heart of china,s Built and Road. DAWN, pp. 5-8.
- Cheng, p. (1989). Xinjiang, The Land and the People. . Beijing: New world press.
- Cohen, D. (2013). China pushes ―Silk Road, regional trade on two fronts. China Brief, 40-46.
- Dani. (2014). China,s Religious Policy in Xinjiang: Fueling Violance? Resurgence of Russia and China Problem. Institute for Islamic Strategic Affairs, 14-30.
- Debasish, C. (2005).
- Dillon, M. (1997).
- Fan, A. H. (2009). Migration and Inequality in Xinjiang: A Survey of Han and Uyghur Migrants in Urumqi. Eurasian Geography and Econamic, 120-137.
- Farhad, L. A. (2015). China's Internal Migration Woes. International Affairs Review, US-China Policy Special Issue, 01-04.
- Fayaz, S. (2014). China,s Xinjiang Problem and Pakistan. The Dialogue, 220-240.
- Gardner, B. (2004). Autonomy in Xinjiang: Han Nationalist Imperatives and Uyghur Discontent. Washington: East-West Center Washington.
- Graham, E. & Fuller, S. F. (2003). The Xinjiang Problem. Washington: Central AsiaCaucasus Institute Press.
- Holdstock, N. (2014). Islam and instability in China's Xinjiang. Norway, NORWEF, 45- 60.
- Hyer, E. (2006a). China,s Policy towards Uighur Nationalism. Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs, 76-81.
- Hyer, E. (2006b). China,s Policy towards Uighur Nationalism. Journal of Muslim Minority, 86-96.
- Jamal, N. S. (2011). CHINA'S XINJIANG POLICY: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON THE THEORY OF RELATIVE DEPRIVATION. Malaysian Journal of History, Politics, & Strategic Studies, 147-166.
- Jamil, N. S. (2011). CHINA'S XINJIANG POLICY: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON THE THEORY OF RELATIVE DEPRIVATION. Jebat: Malaysian Journal of History, Politics, & Strategic Studies, 147-166.
- Mackerras, C. (2002). Xinjiang at the Turn of the Century: The causes of Separatism. Central Asian Survey, 287-302.
- Madsen, R. (2009). The Upsurge of Religion in China. journal of Democracy, 40-78.
- Madsen, R. (2010). The Upsurge of Religion in China. Journal of Democracy, 59-69
- Millward, j. (2006). Voilent Separatism in Xinjiang:a Critical Assesment. Policy Studies, 1-60.
- Nicolas, B. (2000). Xinjiang in the Nineties. The China Journal, 65-90
- Razvan, M. (2005). Ethnic Intermarriage in Beijing and Xinjiang, China,. Journal of comparative Family studies, 20-25.
- Sebastian. (2008). China Intellectuals and The Problem of Xinjiang. China Perspectives, 140-150.
- Shichor, J. (2005). Blow Up: Internal and External Challenges of Uyghur Separatism and Islamic Radicalism to Chinese Rule in. Asian Affairs, 132-140.
- SHICHOR, Y. (2005). Blow Up: Internal and External Challenges of Uyghur Separatism and Islamic Radicalism to Chinese Rule in. Asian Affairs, 119-132.
- Wavgh, D. (1-4). The Silk Roads in History. Silk Road Foundation, 2018.
- Wei, S. (2010). China's new Policy in Xinjiang and it's Challenges. East Asian Policy, 58- 66.
- Widyastuti, R. (2013). Paradox, 0n China,s Great Western Development: socia-ethno problem in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonyms Region. International Master,s Program in Asia Pacific Studies, National Chengchi University, 1-8.
- Xiaogang Wu, X. S. (2013). Ethnicity, Migration, and Social Stratification in China: Evidence from XinjiangUyghur Autonomous Region . Michigan: Population Studies Center University of Michigan Institute for Social Research.
- Yusuf, H. (2020, july friday). Silence won,t Play. DAWN, pp. 5-6.
- Zakria, R. (2020, september sunday). Lost in Xinjiang. DAWN, pp. 22-23
- Zenn, J. (2018). Beijing, Kunming, Urumqi and Guangzhou: The Changing Landscape of Anti-Chinese Jihadists. jamsstone Foundations, 4-8.
Cite this article
-
APA : Gul, S., Khan, A., & Alam, A. (2020). China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang. Global Economics Review, V(II), 75-88. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2020(V-II).06
-
CHICAGO : Gul, Shabnam, Ali Khan, and Aftab Alam. 2020. "China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang." Global Economics Review, V (II): 75-88 doi: 10.31703/ger.2020(V-II).06
-
HARVARD : GUL, S., KHAN, A. & ALAM, A. 2020. China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang. Global Economics Review, V, 75-88.
-
MHRA : Gul, Shabnam, Ali Khan, and Aftab Alam. 2020. "China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang." Global Economics Review, V: 75-88
-
MLA : Gul, Shabnam, Ali Khan, and Aftab Alam. "China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang." Global Economics Review, V.II (2020): 75-88 Print.
-
OXFORD : Gul, Shabnam, Khan, Ali, and Alam, Aftab (2020), "China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang", Global Economics Review, V (II), 75-88
-
TURABIAN : Gul, Shabnam, Ali Khan, and Aftab Alam. "China's Built and Road Initiative: Challenges and Opportunities in Xinjiang." Global Economics Review V, no. II (2020): 75-88. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2020(V-II).06
